Smart Sensors and Their Impact on Control Systems
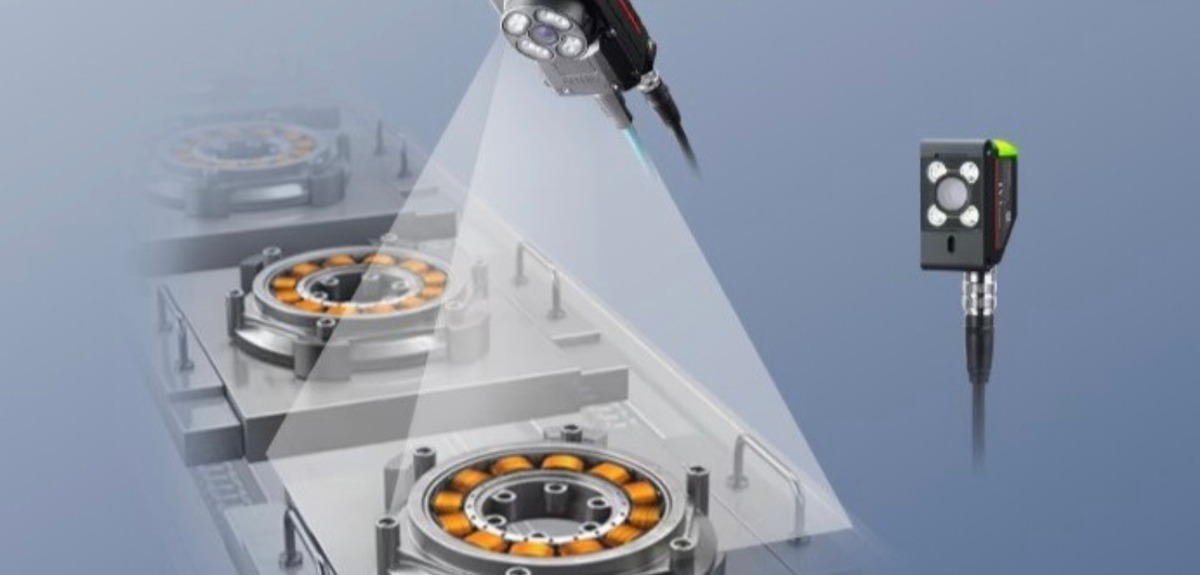

Modern control systems need smart sensors as their essential elements during this period of Industry 4.0 development. Smart devices from intelligent technology sources transform data acquisition and management throughout multiple sectors while initiating an automated period of response-driven operations with real-time performance tracking. Smart sensors differentiate from previous devices because their microprocessor units and communication tools integrate within their design. Smart sensors combine detection capabilities of environmental changes with their power to evaluate situations and transform their responses automatically.
The strategic position of smart sensors gives control systems their key ability to optimize operational speed together with safety and system response capabilities. Conductor systems now perform with improved efficiency, thanks to smart sensors which function throughout production fields as well as within power grid networks alongside healthcare systems. The combination of advanced capabilities results in fewer human mistakes, while speeding up both decision-making periods and predictive maintenance functions and self-regulation mechanisms which makes these sensors crucial for current rapid data-intensive environments.
What Are Smart Sensors?
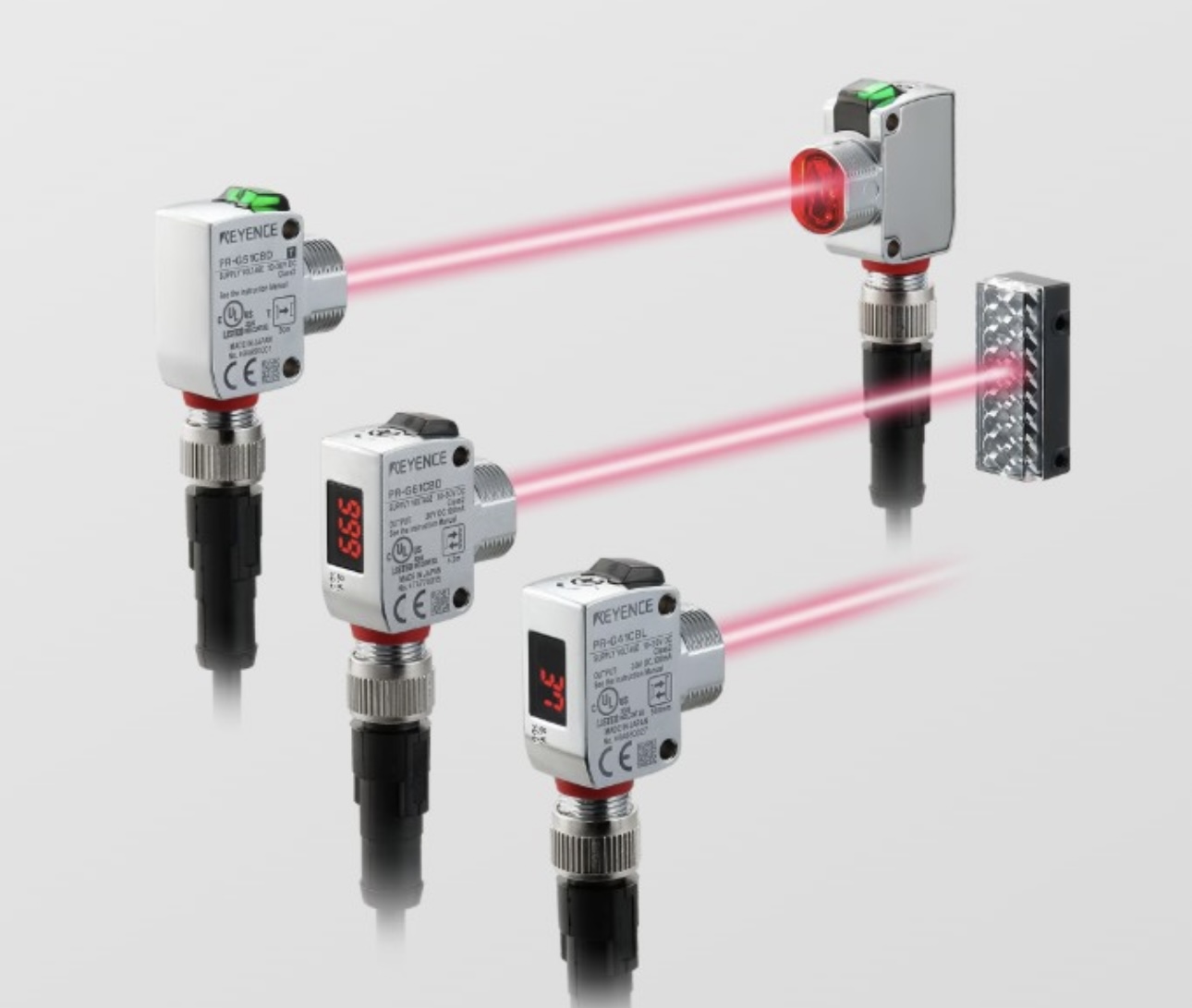

The category of smart sensors includes modern detection devices that surpass basic input detection capabilities which normally include temperature, pressure, movement and light detection. A smart sensor's components include embedded processors and software together with connectivity features which help it process collected data and make instantaneous decision commands for other devices. Smart sensors perform data analysis internally, since they come with processing capabilities unlike conventional sensors that need external systems. The integrated features of smart sensors enable self-diagnostic testing, as well as self-calibration functions which are enhanced by machine learning algorithms for environment adaptation over time. Modern control environments rely on their capability to exchange information with other devices through Bluetooth and Wi-Fi as well as IoT protocol systems. Modern smart systems rely on smart sensors to perform three crucial functions which make precision and automation possible at a higher level.Impact of Smart Sensors on Control Systems Smart sensors deliver meaningful changes to control systems because they enhance system qualities such as operational speed while creating systems that are highly dependable and adaptable. Various sectors experience these changes from smart sensors as illustrated in the following list:
1. Industrial Automation
Manufacturing operations depend on smart sensors as their primary component for industrial automation. Such sensors gather data about machine functioning alongside automatic malfunction alerts which allows equipment performance predictions through analyzing trends in device behavior patterns. Their implementation enables reduced equipment stoppages that safeguards everyone while raising operational output. The sensors serve vital functions in robotic systems as well as CNC machines and automated assembly lines. The control system uses this capability to update automatically thus maintaining ideal production settings.
2. Building Automation and Smart Homes
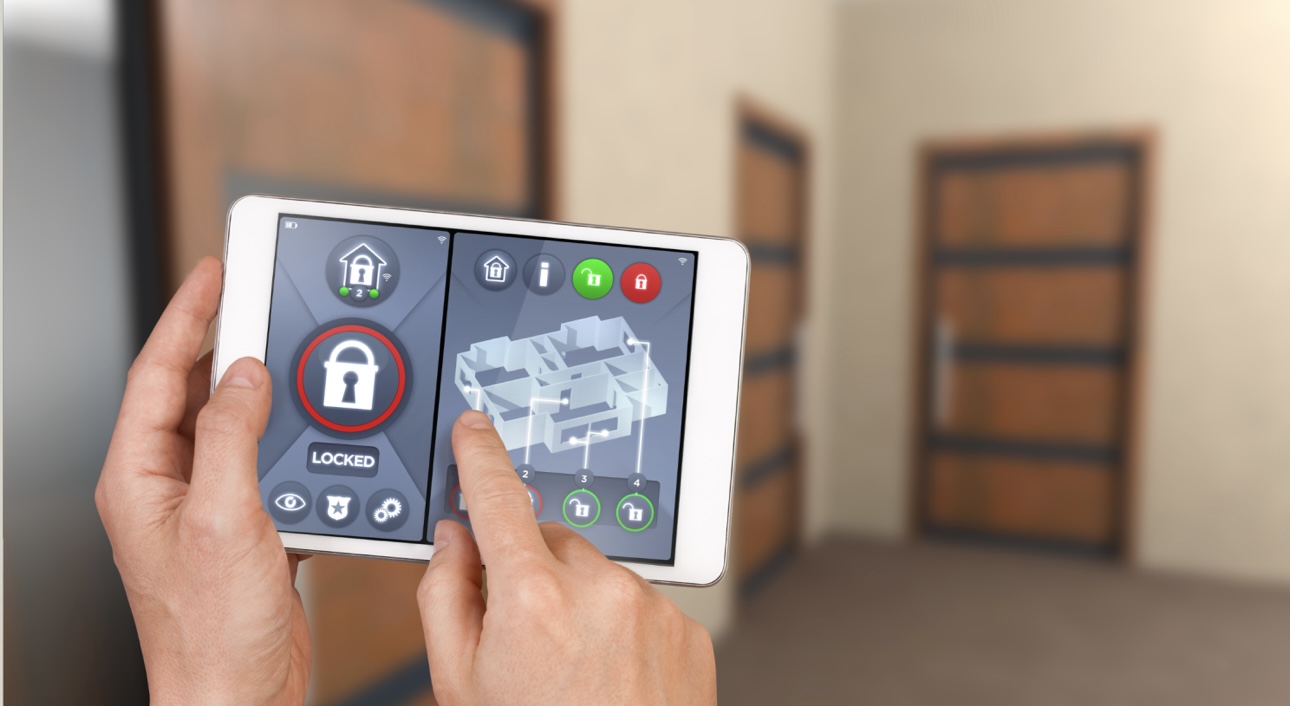

The heating ventilation air conditioning (HVAC) system combined with security functions and lighting controls become automated through modern building management systems (BMS) with smart sensors installed. Occupancy sensors track building usage to automatically control lighting systems and temperature controls which leads to better energy conservation. Modern thermal regulators and smoke detectors feature environmental detectors along with wireless connectivity that easily connects to mobile applications through cloud servers.
3. Smart Cities and Intelligent Traffic Systems
Traffic management systems leverage sensors for monitoring both traffic vehicles and walking pedestrians. Smart traffic lights that contain infrared sensors and motion or pressure sensors enable them to adjust their operation time for better traffic flow. Sensors installed on roads help maintain safety by both observing unexpected driving behavior and detecting sudden accidents during actual driving. Smart cities implement smart streetlights combined with parking sensors and environmental monitoring nodes that integrate with control systems for urban efficiency.4. Healthcare Monitoring Remote healthcare and wearable devices heavily depend on smart sensors for their operation. Patients benefit from devices that seamlessly monitor vital signs using smartwatches and implantable sensors to detect abnormalities which trigger data transmissions. The expansion of Internet of Medical Things(IoMT) technology boosted the adoption of medical devices supplied with sensors for both healthcare facilities and domestic use. These devices enhance clinical results because they trigger emergency interventions during critical times.
5. Environmental and Agricultural Monitoring
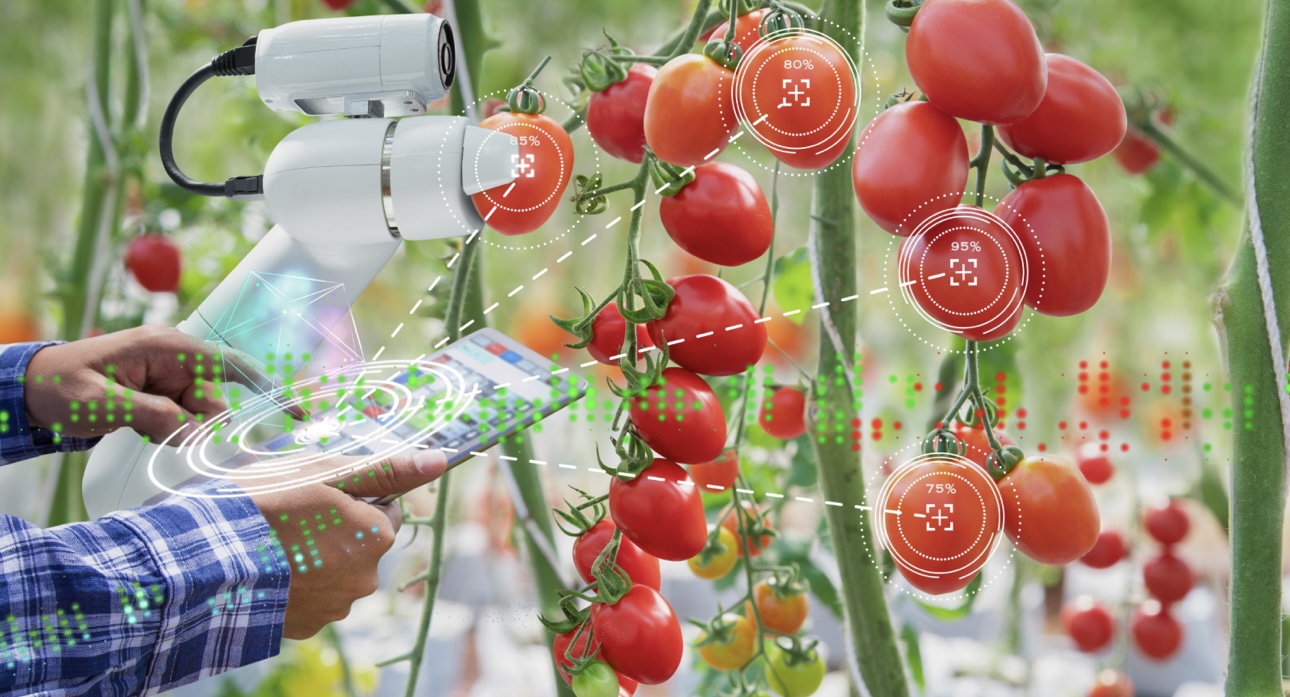

Smart sensors are used for continuous environmental observation of factors including air quality together with water purity and soil moisture levels and climate monitoring. The combination of soil sensors with drones enables agricultural drone operators to evaluate crop health, while the sensors determine irrigation needs of agricultural lands. Monitoring systems incorporated with these sensors become more efficient while reducing waste stream and meeting all environmental regulations in agricultural precision applications. Technological Enablers of Smart Sensors Smart sensors have become more advanced because of multiple technological developments that boost their efficient performance and intelligent operation in control systems.
Market Intelligence News & Insights:
North American Robot Orders Hold Steady in Q1 2025 as A3 Launches First-Ever Collaborative Robot Tracking
 Robot orders in North America remained essentially flat in the first quarter of 2025, with companies purchasing 9,064 units valued at $580.7 million, according to new data released by the Association for Advancing Automation (A3). Compared to Q1 2024, this represents a 0.4% increase in units ordered and a 15% rise in order value, signaling continued demand and increased investment in higher-value automation systems.
Robot orders in North America remained essentially flat in the first quarter of 2025, with companies purchasing 9,064 units valued at $580.7 million, according to new data released by the Association for Advancing Automation (A3). Compared to Q1 2024, this represents a 0.4% increase in units ordered and a 15% rise in order value, signaling continued demand and increased investment in higher-value automation systems.
1. Integration with AI and Machine Learning
The primary advancement that enables smart sensors results from artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms integration. The capacity of smart sensors to examine extensive datasets immediately has developed to where they learn distinctive patterns which improves their decision-making precision. ML algorithms enable industrial turbines to identify normal operational variations from signs that indicate mechanical failure through vibration sensor data analysis. This predictive model enables system maintenance preventing equipment breakdown, while it aids automated control systems in requiring less human supervision.
2. Wireless Connectivity and IoT Integration

Wireless communication serves as an essential enabler in the control systems architecture. Smart sensor technology requires support for Wi-Fi along with Zigbee, LoRaWAN and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) among other IoT protocols following the Internet of Things (IoT) increase.The wireless connectivity enables straightforward installation of smart sensors into control systems even when no major wiring is necessary. The capability of business systems to share information in real-time exists through IoT gateways which create access to cloud platforms so control systems become more responsive with unified monitoring capabilities.
3. Miniaturization and Low Power Consumption
Smart sensors became smaller through the developments of MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems). The recent development of small modern sensors with compact shape and power-efficient functionality allowed these devices to integrate inside wearable health systems, robotic platforms and human body applications. These devices maintain long-term operation in distant sites, thanks to their low energy requirements which makes them suitable for various industrial applications.
Challenges in Smart Sensor Adoption
1. Cybersecurity Risks
Protection of smart sensor data must prevent unauthorized interception and any form of alteration during transmission. Industrial control systems (ICS) face cyber threats which produce two main effects: malfunctioning equipment and safety hazards for the public. Smart sensor manufacturers now focus on cybersecurity because it requires encryption techniques and boot security protocols and firmware maintenance.
2. Lack of Standardization
Interoperability between sensors produced by different manufacturers becomes difficult because there is no common standard. Smart sensors prove difficult to integrate into existing control systems because of this limitation which affects legacy infrastructure implementation. Open protocols such as OPC UA together with MQTT standards are becoming more popular to solve this problem but their acceptance remains inconsistent between different industries.
3. High Initial Costs
The modern smart sensor technology leads to reduced operational costs in the long run yet might discourage small and medium-sized enterprises because of their upfront implementation expenses. The technological development along with increasing production scale will lead to decreasing costs and making the technology more affordable.Future Outlook and Trends Smart sensors show encouraging future prospects since both technological advancement and market adoption are increasing in numerous sectors. The following patterns will define their future advancement:
1. Market Growth Projections
Statistics from market analysts indicate future market expansion of smart sensors will reach $45.7 billion by 2030 from the 2023 base of $25.5 billion. The marketplace expands due to escalating sector needs for industrial automation combined with healthcare requirements, renewable energy systems, and consumer electronic applications which need precise data-driven control systems.
2. Rise of Edge Computing
Cloud computing platform identifies itself as a necessary element for creating smart sensor systems. The processing of data in localized locations near sensors offers superior real-time response and decreased latency when compared to cloud-only systems. The time span of one millisecond stands crucial for operational safety and performance in industrial applications, including autonomous vehicles and smart grids as well as industrial robotics.
3. Sustainability and Green Control Systems
The fundamental role of smart sensors is to drive sustainability initiatives. Resource management becomes more efficient while environmental compliance becomes practical because of their deployment in energy metering systems, leak detection applications, and emissions monitoring tasks. Industry achievement of global sustainability goals depends heavily on smart sensors which will develop efficient control systems that minimize waste and preserve energy.
Conclusion
Modern control systems experience a transformation because smart sensors allow continuous data analysis and adaptive decision processes with automated response capabilities. These devices find use in multiple industries including manufacturing, healthcare, smart cities, and agriculture to modify human living along with workplace operations and environmental interactions.The innovation beyond automation and sustainability and digital transformation will result from smart sensors that evolve in intelligence and connectivity as well as affordability. Every organization needs to integrate smart sensors within control systems to enhance operational efficiency because it has become mandatory for maintaining future readiness.







Leave a Reply